Write4U
Valued Senior Member
Continuing our research on the emerging science on the role microtubules play in cellular growth and disease.
Recent Approaches to the Identification of Novel Microtubule-Targeting Agents
This paper is a comprehensive overview of emerging role of microtubules in treatment of various medical conditions.
The following excerpt is technically above my pay-grade, but it does confirm my initial "recognition" and "anticipation" of the importance microtubules will play in future medicinal science.
I am sure that "learned minds" will recognize the actual state of the scientific discoveries that microtubules are beginning to play in greater scheme of things. You be the judge.
some excerpts:
https://www.frontiersin.org/files/A...-841777-HTML/image_m/fmolb-09-841777-g002.jpg
PROTACs
[quote[PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs) is a technology that holds great promise for overcoming drug resistance problems as it allows the inactivation of the target protein by inducing its complete degradation rather than its sheer inhibition (Garber, 2021). [/quote]
And a scientific conclusion that I predicted several years ago.
Conclusion
And this is what I intended to share with interested readers and I have had some encouragement, but alas, my research has fallen on deaf ears from sceptical "learned minds" and years of research in this new area of scientific study are now in a closed thread and not open to further news from an exciting new area of medical inquiry. Too bad!
Below is the link to the entire paper and related science, including downloadable pdf
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2022.841777/full
Recent Approaches to the Identification of Novel Microtubule-Targeting Agents
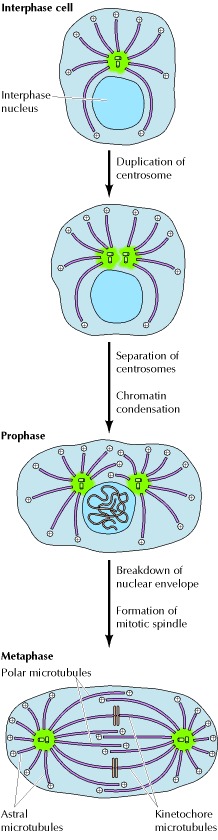
.....Consistent with their involvement in core cellular processes, affecting microtubule assembly results in cytotoxicity and cell death. For these reasons, microtubules are among the most important targets for the therapeutic treatment of several diseases, including cancer.
The vast literature related to microtubule stabilizers and destabilizers has been reviewed extensively in recent years. Here we summarize recent experimental and computational approaches for the identification of novel tubulin modulators and delivery strategies. These include orphan small molecules, PROTACs as well as light-sensitive compounds that can be activated with high spatio-temporal accuracy and that represent promising tools for precision-targeted chemotherapy.
This paper is a comprehensive overview of emerging role of microtubules in treatment of various medical conditions.
The following excerpt is technically above my pay-grade, but it does confirm my initial "recognition" and "anticipation" of the importance microtubules will play in future medicinal science.
I am sure that "learned minds" will recognize the actual state of the scientific discoveries that microtubules are beginning to play in greater scheme of things. You be the judge.
some excerpts:

https://www.frontiersin.org/files/A...-841777-HTML/image_m/fmolb-09-841777-g002.jpg
PROTACs
[quote[PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs) is a technology that holds great promise for overcoming drug resistance problems as it allows the inactivation of the target protein by inducing its complete degradation rather than its sheer inhibition (Garber, 2021). [/quote]
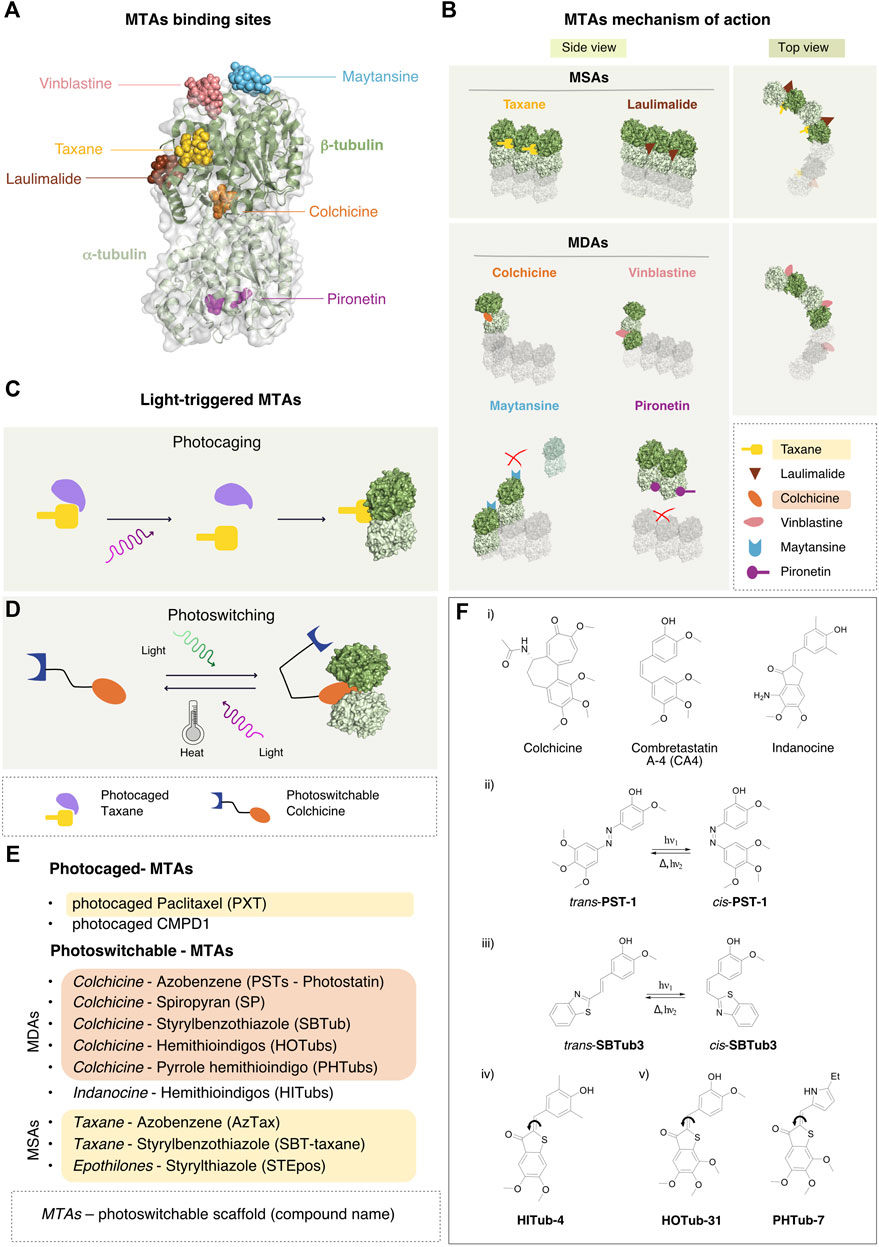
PROTACs are bifunctional molecules featuring an E3 ubiquitin ligase moiety tethered to a ligand of the target protein of interest via a linker of optimal length. The association of the ligand moiety of the PROTAC with the protein of interest promotes ubiquitination of the target protein and its degradation by the ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS).
Recently, an attempt to develop the first tubulin-targeting PROTAC has been made (Gasic et al., 2020). The validity of this approach is corroborated by the observation that a number of compounds that are known to bind covalently to different cysteines on β-tubulin promote tubulin degradation (Yang et al., 2019). The authors designed different degrader molecules, all of them featuring a E3 ubiquitin ligase Cereblon (CRBN) moiety and either a monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) scaffold or a combretastatin A-4 (CA4) scaffold as tubulin-binding moiety, the former binding at the interface between α and β-tubulin, the latter binding only to β-tubulin.
..... moreHowever, neither strategies resulted in tubulin degradation. While the authors conclude that tubulin may be resistant to degradation by CRBN-recruiting PROTACs, they also suggest that the use of other E3 ligases or the use of a different tubulin-binding moiety may eventually lead to a successful tubulin degradation by different PROTACs. It is also conceivable that by combining photoactivation with protein degradation, the use of PHOTACs (PHOtochemically TArgeting Chimeras) may enable a precise spatio-temporal control of degraders by light (Reynders et al., 2020) and could represent a promising approach to high precision modulation of microtubule stability. Madhukar et al., 2019).
....... moreBANDIT integrates more than 20 million data points from such diverse data types as drug efficacy, post-treatment transcriptional responses, drug structures, reported adverse effects, bioassay results, and known targets. This integrated approach allows the identification of drugs that share the same target much more accurately than approaches that use single data types. Using this approach on microtubules, the authors initially identified a set of 24 structurally diverse orphan small molecules, which they tested experimentally on breast cancer cells. Of these 24 compounds, 14 were active on microtubules. Interestingly, only nine of these 14 compounds were also identified using structure-based only prediction methods. Tested on an ovarian carcinoma cell line that is resistant to Eribulin, an FDA approved MDAs, the authors identified three compounds that show good microtubule depolymerization activity against these cells, thus overcoming the Eribulin resistance problem.
And a scientific conclusion that I predicted several years ago.
Conclusion
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2022.841777/full#h5Because of its essential role in mitosis, tubulin is a fundamental target in drug discovery and an important benchmark for testing new cancer therapeutic approaches and ideas. This continuous quest for novel microtubule interactors is also justified by the drug resistance problem, which is often hampering the clinical efficacy of the current gold standard MTAs such as paclitaxel and vinblastine. Here we reported some of the most interesting and innovative recent approaches to MT modulation. It is likely that some of them will continue to be explored to identify new MTAs that may eventually provide viable alternatives to the current therapeutic protocols.
And this is what I intended to share with interested readers and I have had some encouragement, but alas, my research has fallen on deaf ears from sceptical "learned minds" and years of research in this new area of scientific study are now in a closed thread and not open to further news from an exciting new area of medical inquiry. Too bad!
Below is the link to the entire paper and related science, including downloadable pdf
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2022.841777/full
Last edited: